Pain in the joints of the fingers when bending is most often caused by age-related changes, as well as irreversible processes in the body that provoke negative manifestations and the development of a state of discomfort in the patient. Such a pathology requires mandatory medical intervention, which includes all methods based on the causes of pain symptoms in the upper extremities.
Causes of pain
Fingers must be treated if the factors that provoked such a problem have been identified. As a rule, doctors divide pain in the hand joints into 2 groups (mechanical and inflammatory).
Mechanical pain is accompanied by a local, mildly expressed inflammatory process, which "erases" the picture of the disease. Often, patients do not pay attention to these symptoms, unlike inflammatory pain. In this case, there is stiffness of movement in the morning, which can last more than 1 hour. The pain decreases slightly during physical activity.
We list the diseases that can cause such symptoms.
Rheumatoid arthritis
With the development of rheumatoid arthritis, small joints are affected, but it is quite possible that internal organs and large joints are involved in the pathological process. Rheumatoid pain is accompanied by swelling and redness of the metacarpal phalanx of the middle and index fingers.
With this disease, the fingers become very painful when bent and a similar symptom is observed on the second hand. A characteristic symptom of rheumatoid arthritis is pain that occurs immediately after waking up, while the pain subsides at night.
Psoriatic arthritis
This disease mainly affects the skin and the pain appears mainly in the distal phalanges. In psoriatic arthritis, there is severe swelling of the fingers, which become bluish in color. In addition, with this disease it is quite difficult to straighten the thumbs.
Infectious arthritis
In infectious arthritis, there may be no systemic disorder, but it is characterized by the appearance of an acute attack of pain when bending the finger, which may last from 2 to 3 hours to 2 to 3 days. Sometimes chills and hyperthermia are present.
Drop
This disease is the most common, but in most cases, patients completely unexpectedly discover the real reason why their finger joints hurt when bending, after clarifying the diagnosis. Most often, the disease occurs in people over 50 years of age.
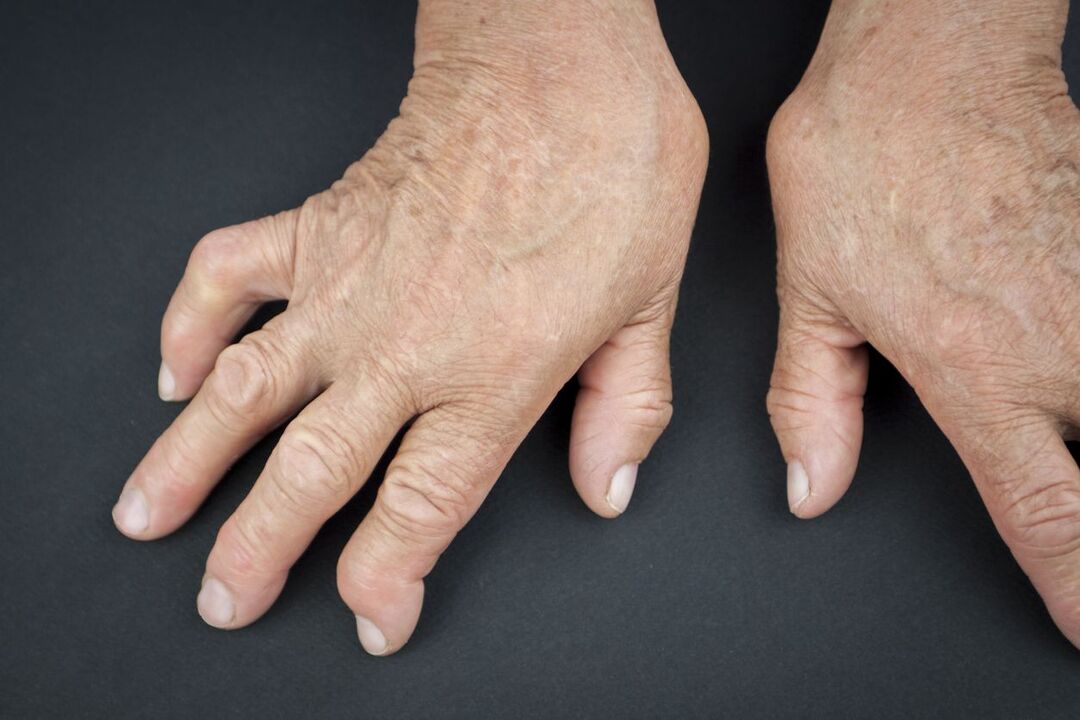
The main reason for the progression of gout is a violation of uric acid metabolism, which is quite difficult to remove from the body, depositing in cartilage and joints, creating a serious obstacle to their normal functioning. Characteristic signs of gout include intense, burning pain.
Osteoarthritis
Among the most common reasons for the development of osteoarthritis are hereditary factors, as well as disorders of metabolic processes in the body, activities associated with increased physical activity, etc. In most cases, osteoarthritis occurs in mature women due to hormonal changes.
A characteristic symptom of the disease, in addition to unbearable pain in the joints of the hand, is the occurrence of swelling and subcutaneous nodules, which cause deformation of the fingers and thickening of the middle part.
Stenosing ligamentitis
This pathological process can have symptoms similar to arthrosis and arthritis, therefore, x-ray examination is necessary to clarify the diagnosis. Clinical manifestations are quite typical: it is painful for the patient to straighten and bend their hands, and in some cases the clenched palm can get stuck. In addition, the extension of the fingers is accompanied by characteristic clicks.
Rhizarthrosis
If pain appears in the thumb joint, then, most likely, such a condition may indicate rhizarthrosis, which manifests itself as intoxication, previous infections and various types of injuries.
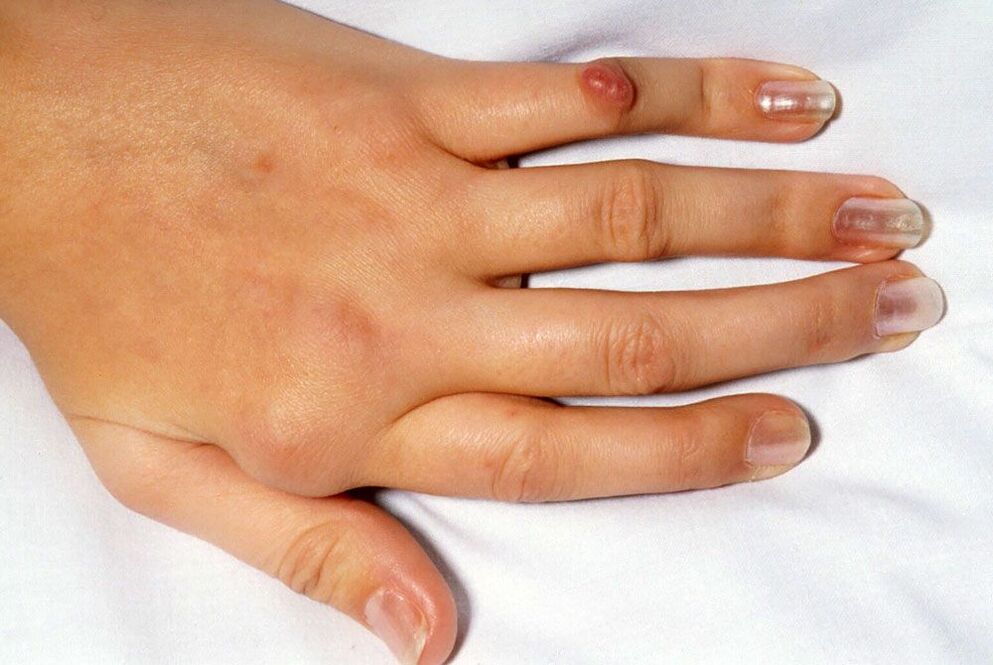
During the initial examination of the patient, the localization of pain is determined, which intensifies under specific loads (turning a key, turning a handle, opening a screw cap, etc. ). At the initial stage of the development of the disease, the finger hurts when bending only after physical exertion, but the progression of rhizarthrosis causes the pain to begin to bother the patient even at rest. Gradually, deformation of the joint occurs with limitation of motor activity.
In addition to all of the above diseases, the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, most often diagnosed in young patients, can cause discomfort in the thumb or index finger area. This is due to prolonged sitting at computers, during which the ulnar nerve is compressed, which in turn leads to the development of pain in the fingers.
Symptoms of pathology
Serious signs of the presence of diseases that can lead to a series of negative consequences are:
- nodular neoplasms in the tendon area;
- creaking of fingers when moving;
- pain on palpation of the hands;
- sharp, piercing pain and impairment of fine motor coordination;
- compaction in the folds of the fingers and hyperemia of the inflamed area;
- inability to squeeze little fingers;
- local and local increase in body temperature;
- increased nighttime pain in the arms;
- Special attention should be paid if the finger becomes suddenly swollen and deformed.
If the patient discovers such manifestations, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary, who will carry out diagnostic measures and prescribe complex therapy to alleviate painful symptoms and the inflammatory process.
Diagnostic methods
Patients who experience pain in their hands, especially after sleeping, should undergo a course of therapy, but only after clarifying the reasons for the development of the pathological condition.
In this case, diagnosis involves the following methods:
Radiography
The most informative way to determine tumor-like neoplasms, various injuries and inflammatory processes in the joints of the fingers and hands is an X-ray examination.
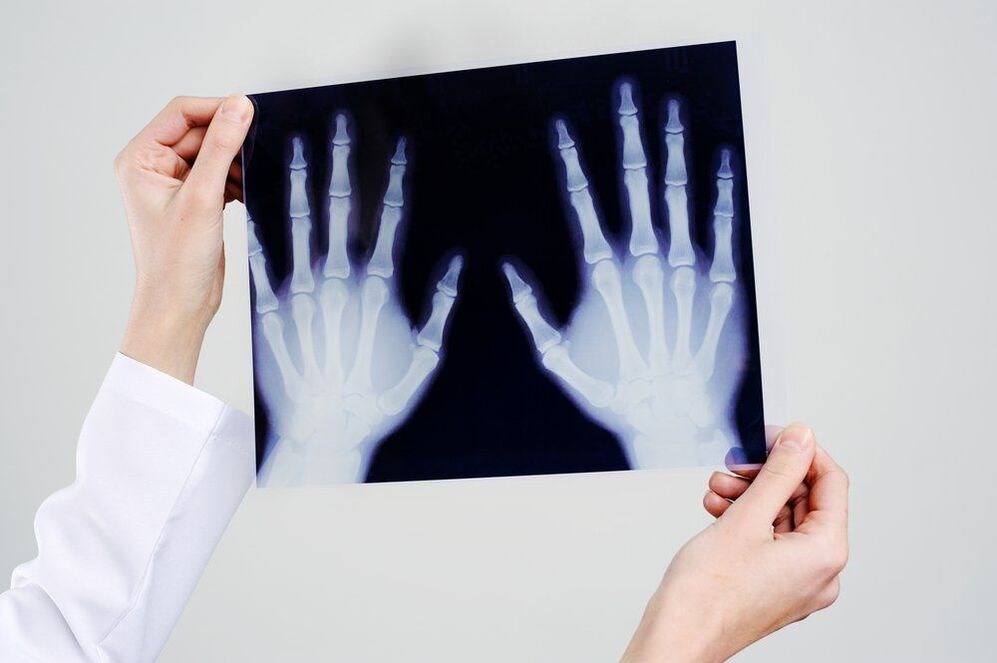
Despite the high efficiency of radiography, it has a significant disadvantage - the inability to assess the condition of soft tissues
Ultrasound
Using ultrasound, the presence of an inflammatory process in the tissues is determined and the consequences of joint damage are identified. This procedure is most effective for synovitis, arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis and osteoarthritis. In cases where the middle finger is numb and painful, it is possible to perform an ultrasound examination of the blood vessels to determine the violation of blood flow in the upper extremities.
Computed tomography
To obtain a more accurate picture of the pathology of bone tissue and joints, it is recommended to perform a computed tomography scan, which takes 5-7 minutes and is well tolerated by patients. The difference between computed tomography and radiography is that the information obtained is displayed directly on the monitor screen, which allows you to obtain more reliable information.
Electrospondylography
A highly effective and universal examination method is electrospondylography, which has been used in medicine relatively recently. This test can detect early damage to the area of the spine responsible for the functionality of the upper extremities, including the fingers.
MRI
MRI is considered an informative and accurate study, which is why it is often used in the diagnosis of various diseases, including joint ones. The pathological process is determined using electromagnetic waves, which form an image of the tissue, the location and degree of development of the inflammatory process.
In addition, blood tests (clinical and biochemical), urine tests for the presence of blood and proteins are prescribed, as well as a joint puncture for persistent pain in the fingers.
Important! It is necessary to take into account that fingers can hurt for various reasons, however, only a highly qualified specialist should correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe individual pain treatment.
Treatment
If painful symptoms occur, the main therapeutic measures should be aimed at eliminating the causes of the development of the pathological process.
Complex therapy includes drug therapy and treatment with folk remedies.
Drug treatment
To alleviate the pathological process, the doctor prescribes the patient a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which, in addition to reducing inflammation, relieve painful symptoms and reduce tissue swelling.
For osteoarthritis, prolonged use of chondroprotectors is recommended to nourish the cartilage and prevent its further destruction. These medications help prevent the disease from recurring.
In cases where there is unbearable pain in the fingers and the inflammatory process is at an advanced stage, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. They quickly relieve symptoms of inflammation and regulate metabolic processes in the body, thereby accelerating tissue regeneration.
If the main cause of painful symptoms in the toe area is a bacterial infection, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and antibacterial agents, based on the severity of the symptoms and the body's sensitivity to a group of these drugs.
Important! You should not self-medicate as this may cause allergic reactions and side effects. At the beginning of therapy, restoration of damaged joints is necessary. And only in the calm phase is it recommended to resort to auxiliary methods (physiotherapy, hand massage, gymnastics, etc. ).
Physiotherapy
Pain in the joints of the hands indicates a violation of the functionality of the body as a whole and, in particular, the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes. That is why, first of all, it is necessary to limit physical activity and reduce physical stress on the joints.
Physiotherapeutic measures include resonance therapy, electrosleep and electrophoresis with the addition of novocaine. Also, during the period of remission, therapeutic exercises, the use of mud, hydrogen sulfide and radon baths, as well as massage, including manual, have a positive effect.
Diet
Adequate nutrition is of no small importance in preventing the occurrence of pain, as the body must receive a sufficient amount of microelements such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, iron and vitamins, mainly through food.
Products that can reduce finger joint pain when bending:
- Fish oil and linseed oil. These products contain large amounts of omega-3 fatty acids, which improve the condition of the vascular system and participate in the normalization of fat metabolism.
- Apple cider vinegar, as it enhances the removal of salts and participates in the blood alkalinization process.
- Radishes, lettuce and nuts.
- Egg yolk, juice and pomegranate fruit.
- Black currant and fig.
- Ginger and cauliflower.
- Low-calorie cheeses and olive oil.
It is necessary to limit (and in some cases completely exclude from the diet) high-fat dairy products, sweet and high-calorie foods. Smoked meats, alcoholic beverages, coffee, strong tea, as well as products containing oxalic acid.
Folk remedies
At the initial stage of the disease, pain can be treated with traditional medicine, for example, with a compress of kefir and chalk, diluted to a pasty state. Oatmeal, pre-boiled and slightly cooled, has a similar effect.
You can prepare a cream for massaging your hands from an equal amount of crushed bay leaves and juniper pine with the addition of softened butter to this powder. After mixing the ingredients well, the ointment can be used for its intended purpose.
In case of exacerbation of painful symptoms, it is recommended to mix 1 tbsp. a spoonful of olive oil with 5 drops of garlic juice and drink the prepared mixture in the morning, 30 minutes before breakfast. The procedure must be repeated for 3-4 days.
Sudden and intense pain in the finger interferes with the performance of daily tasks, causing unbearable suffering to the patient. Such manifestations should not be neglected, as they may indicate a number of serious illnesses that can cause painful symptoms.
Only early diagnosis and timely intervention by an experienced doctor make it possible to determine the etiology of the disease, on the basis of which the doctor decides how and with what to treat in order to obtain the most positive result. With timely intervention, the prognosis for full recovery is favorable.















































